Many hazards were involved in the operation of seagoing bulk carriers. It is essential to be careful and vigilant in all matters pertaining to shipboards. This website provides information to the shipping community about the best way to load and unload bulk cargo. However, it must not go beyond the limits that are set by the classification society. It's vital to reduce the risk of stressing the structure of the ship and complying with all essential safety measures for a safe sea voyage. The detail pages on our website cover various bulk carrier-related topics that could be helpful to those working onboard and those who working ashore at the terminal.
The general characteristics of bulk ships that travel by sea.
Bulk carriers have a single deck and include top-side tanks and the hopper tank. They can carry bulk cargo, which is a single product. Solid bulk cargo means any material, other than gas or liquid composed of particles, granules or any other larger piece of material, generally uniform in composition, which is directly loaded into the cargo areas of ships without immediate confinement. Sugar, grain and bulk ores are examples of such dry cargo. The bulk carrier is a vessel that is primarily used for transporting bulky or liquid cargo. It also includes tankers. The term is typically used for ships that transport bulk goods that are solid. This includes grains and similar agricultural products. Have a look at this bulk ship url for more.
What Is A Bulk Carrier What Are The Main Features Of Bulk Carriers:
"A ship which is intended primarily to carry dry cargo in bulk, including such types as ore carriers and combination carriers"
-Carrying capacities vary between 3,000 and 300,000.
-Average speed between 12 and 15 knots
-Single deck ships, ie no tweendecks
Carriers of small- to medium-sized bulk (carrying a maximum of 40,000 tonnes) are typically equipped with equipment for handling cargo. Larger vessels rely on facilities that are located on shores, which allows the loading and unloading of cargo.
The dimensions of cargo hold are typically big with no obstructions. They also come with larger hatches that allow for easy loading/unloading.
Ballast holds are a standard element on bulk carriers. It can be used to ballast voyages in order to improve stability. A couple of additional holds are possible to ballast in part at port, but only
They are available as one pull, or stacking (piggyback) and type steel hatch covers.
There are four types and sizes of ballast tanks:
Sloping topside wing tanks
Tanks with a sloping bottom side.
Double bottom tanks
Peak and post peak water tanks.
Is it solid bulk cargo? Any substance that is not liquid or gas, consisting of a mix of particles, granules , or any larger pieces of material, generally of uniform composition and loaded directly into the cargo space without any intermediary method of containment. Cargoes transported by bulk carriers include "clean" foodstuffs and "dirty" minerals. They may react one another and with water sources that are contaminant, such as. This is why it is vital to prepare the cargo spaces for the specific cargo. Surveyors are often called upon to examine the space and determine if the space is suitable for loading. To avoid contamination, it is vital that any leftovers left by a previous cargo be taken away. The damage to bulk cargoes can be due to water. Thus it is not enough that the hold be dry in order for cargo to be able to enter, but hatch covers must be watertight, or in the event of necessity, sealed to prevent ingress of water. Every fitting (ladders or pipe guards, as well as bilge covers) in the hold should be examined. You should inspect every fitting inside the hold (ladders,pipe guards,bilge covers...) to ensure that they are in good functioning order. The equipment could cause severe delay and damage to conveyor belt systems. Inadvertent discharge of cargo can result in the ship being held responsible. Have a look at this bulk carriers specialist for more.
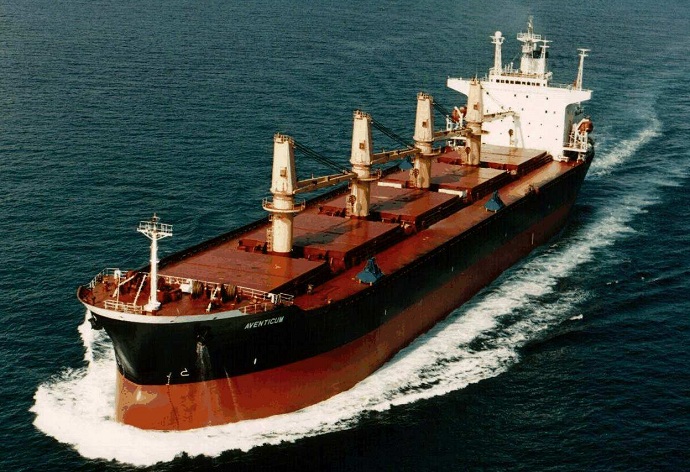

Bulk Carrier, Bulker A vessel designed to carry dry cargo, loaded onto the vessel without any containment other than the ship,s boundaries and is distinct from the bulk carrier that is liquid or tanker. Bulk carriers that are conventional have only a single deck that has a one skin, double-bottom, topside and hopper side tanks. Bulk carriers are designed to transport bulk cargo of any size either light or heavy, and carry a maximum capacity of 450 lbs. The loading, carriage and discharge of dry bulk cargo aren't as straightforward or simple as people think.
Gearless Bulk Carrier
Many bulk cargoes may have hazardous properties or undergo changes in transport. The ship can be easily damaged due to improper loading e.g. It is possible for a ship to bow if not loaded properly. This is known as stress. If the weather is bad it can lead to life-threatening problems at sea. Other cargoes can also be affected by residues from prior cargoes. Certain bulk cargoes are vulnerable to damage from water. cement power. It is hard to determine the quantities and weights of cargoes that are loaded and unloaded. These variables can have significant implications on the way bulk cargoes are transported safely. Discharging bulk cargo using? Bulk cargoes have an inherent tendency to form a cone whenever they are loaded when conveyor belts and similar systems are not monitored and controlled. The angle formed by this cone is known as the `angle of repose'. It varies for each cargo. Iron ore cargoes for instance, will make an angle-shaped cone. The cargo that is able to move around freely will result in the cone with a narrow angle. Low angles of repose could cause the cargo to shift in transit. Certain cargoes require bulldozers to distribute the load across the storage areas. Many dry-bulk carriers are dependent on shoreside facilities for cargo discharge or loading. However bulk carriers could be able to self-unload using conveyors beneath the cargo holds or on decks.
